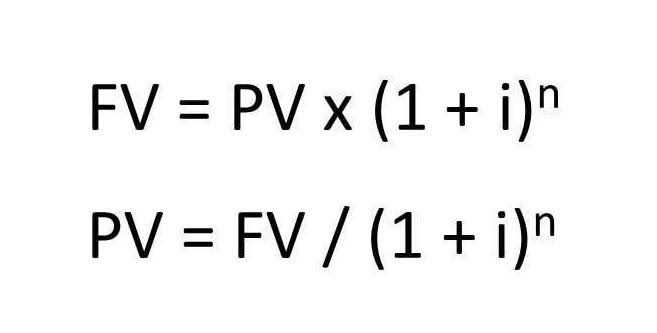Financial statements prepared using the Historical Cost Principle provide a clear and consistent basis for analysis. In the 15th century, Italian mathematician Luca Pacioli cost principle developed the double-entry bookkeeping system based on the historical cost principle. This system required that every transaction be recorded in two accounts, one representing the asset or expense at its original cost. However, the Cost Accounting Concept does not reflect the current market’s real value of assets or liabilities. Using this concept, the users will get confused, especially when the market value of assets or liabilities is significantly different from the original costs.

Intangible Assets
- Valuation may be at historical cost, fair value, notional value, intrinsic value, etc.
- If you’re a responsible accountant or small business owner, you need to manage and track your firm’s assets in a standard way that everyone knows.
- The fair value of an asset is the current price you could potentially sell the asset for.
- In conclusion, the historical cost is used to measure the asset’s value for financial purposes, but not all assets can be measured by their historical costs.
- Over time, the value of assets can fluctuate significantly due to market conditions, technological advancements, or wear and tear.
- This can result in financial statements that do not reflect the actual economic value of a company’s assets and liabilities.
The fair value is used to determine the value of a businesses assets if they were to sell them to potential buyers. Inventory means the items held by a business firm for resale or business use. While the principle is widely accepted in accounting, there are several exceptions where companies may use other valuation methods. The fair value or market value of an asset is the value that the company is expected to receive for selling an asset. For example, a company vehicle might have been in an accident and completely totaled.
Historical Cost vs. Market Value (FMV): What is the Difference?
The historical cost principle provides essential information to stakeholders regarding a company’s financial position and profitability. For instance, it may not accurately represent the current value of assets if market conditions significantly increase their worth. Nonetheless, understanding historical costs and their impact on financial statements is vital for investors, analysts, and company management alike when assessing a business’s overall financial health. Historical cost is a fundamental concept in accounting that plays an essential role in valuing assets for financial reporting purposes. This accounting method calls for recording an asset’s worth on the balance sheet based on its original cost at the time of acquisition. The historical cost principle adheres to the conservatism principle, which aims to prevent overstating a company’s assets’ values (Ballou, 2015).
Historical Cost: An Accounting Principle

This concept is clarified by the cost principle, which states that you should only record an asset, liability, or equity investment at its original acquisition cost. A historical cost can be easily proven unearned revenue by accessing the source purchase or trade documents. A company’s balance sheet should reflect all assets, liabilities, and equities at this cost, regardless of how much they have appreciated over time. Comparing an asset’s current value to its original price shows how it has performed financially over time. As a result, it differs from the fair market, reflecting the asset’s current value.
Mark-to-market accounting involves recording assets and liabilities at their fair value on a regular basis, which can result in significant changes to financial statements due to market fluctuations. Conversely, the historical cost approach provides more stability by maintaining consistent values regardless of changing market conditions. The cost principle’s influence on financial statements is https://www.bookstime.com/articles/equity-multiplier profound, shaping how companies present their financial health to stakeholders. By recording assets at their original purchase price, the cost principle provides a stable and consistent basis for financial reporting. This stability is particularly beneficial for long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, where the original cost can be easily verified through documentation like invoices and receipts. This verifiability enhances the reliability of financial statements, giving stakeholders confidence in the reported figures.